The Musée de la Grande Guerre, the Museum of the Great War, is located at Meaux, 40 km north east of Paris. The town of Meaux is on the River Marne, the area being the location of a pivotal battle during the First World War.
 |
| Musée de la Grande Guerre Meaux |
 |
| Musée de la Grande Guerre Meaux |
1914
In August 1914 the German Army invaded Belgium triggering the start of World War One. The armies of Germany, France and Britain would clash in the Battle of the Frontiers.
 |
| German Soldier |
The Germans overpowered the allied forces as the advanced through Belgium forcing the French and British armies back to the River Marne.
 |
| French Soldiers |
 |
| British Soldiers |
The allies went on the offensive in the Battle of the Marne in September 1914. The French Army however lacked transport to bring troops to the front. They used Paris Taxis to transport 4,000 men of the 62nd Division to the battlefield north of Meaux. The taxi drivers patriotic fervour did not extend to a free ride, their meters were running for the 50km trip and they were paid by the French Government for the journeys.
 |
| Battle of Marne Taxi |
 |
| Battle of Marne Taxi |
The French and British armies advanced north of the River Marne causing the Germans to withdraw to the River Aisne. There the Germans established defensive positions along the north bank of the river. The British and French were able to force passage across the Aisne, but were unable to dislodge the Germans and both side started to entrench.
This was the beginning of trench warfare that would become synonymous with World War One. The period after the Battle of the Aisne would become known as the Race to the Sea as each side tried to turn each others flank. Neither side achieved this and as the engagements moved north, both sides entrenched at the end of the action.
1915
By 1915 the Western Front was a series of trenches that stretched 700 km from the North Sea to the Swiss Border.
 |
| German Trench |
 |
| French Trench |
 |
| British Trench |
Both sides attempted to break the deadlock in 1915. The Germans in Ypres, French and British in Artois, all attempts failing.
1916
In February 1916 the Germans launched at offensive at Verdun. Their aim being to defeat the French Army by attacking one of the nerve centres of the Western Front causing them to commit their reserves, and achieving victory. It turned out to be the longest battle of the First World War and became a battle of attrition with no decisive result.
To keep the frontline supplied with men and materiel was a major logistical effort during the course of the battle. For the French all movements of troops and supplies to and from the battlefield was along a single road between Bar-Le-Duc and Verdun. The 56 kilometre route became known as La Voie Sacrée, the "Sacred Way", because of it’s importance in sustaining the French defence of Verdun. Along its path passed 6,000 lorries and buses every day, one vehicle passing every 14 seconds.
 |
| French Truck and IJ (former RCT Driver) |
The Battle of Verdun lasted 10 months from February to December 1916. In July an Anglo-French offensive on the Somme failed to achieve a breakthrough. As with Verdun, the Somme became an a battle of attrition as the allies gained ground, but failed to break the stalemate.
 |
| Western Front 1916 Battles |
1917
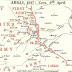
In 1917 attempts by the French and British to break the deadlock failed. France's Nivelle offensive, a plan for rapid victory would end in disaster and mutinies. Early success for the British at Arras, Ypres and Cambrai could not be consolidated.
 |
| Western Front 1917 Battles |
 |
| American Army |
The conduct of warfare was changing. The air warfare and the tank were becoming an integral components of operations.
As the war dragged on into 1918, the allied blockade of German ports was causing food shortages and impacting upon resources to conduct the war. Manpower was lacking to sustain the war effort as casualties mounted. As Germany weakened, American manpower and resources were strengthening the Allies.
To try to achieve victory before the Allies grew too strong, Germany launched a Spring Offensive in order to break the allied line and force a surrender. Their efforts initially achieved significant success, pushing the front line backwards. They were however unable to break the line, it held, Allied forces then counter attacking. The last 100 days of the war began in August 1918, German armies were forced back towards Germany and were ultimately defeated.